Set<E> 인터페이스의 특성
Set<E> 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스들은 데이터의 저장순서를 유지하지않는다.
Set<E> 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스들은 데이터의 중복 저장을 허용하지 않는다.
Set 는 집합 이라는 뜻이다.
Set연산 은 교집합(intersect), 차집합(difference), 합집합(union)과 같은 연산을 할 수 있다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Integer> A = new HashSet<Integer>(); A.add(1); A.add(2); A.add(3); HashSet<Integer> B = new HashSet<Integer>(); B.add(3); B.add(4); B.add(5); HashSet<Integer> C = new HashSet<Integer>(); C.add(1); C.add(2); System.out.println(A.containsAll(B)); // false System.out.println(A.containsAll(C)); // true //A.addAll(B); //A.retainAll(B); //A.removeAll(B); Iterator hi = A.iterator(); while(hi.hasNext()){ System.out.println(hi.next()); } } } | cs |
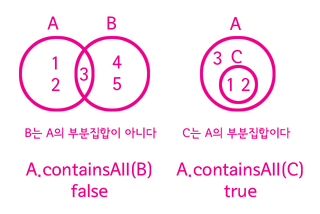
1 2 3 4 | 부분집합 (subset) System.out.println(A.containsAll(B)); // false System.out.println(A.containsAll(C)); // true | cs |
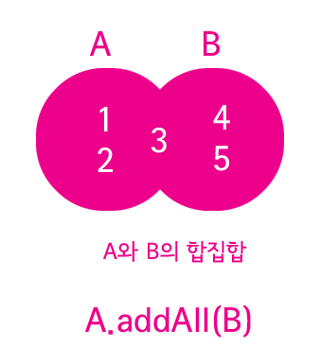
1 2 3 | 합집합(union) A.addAll(B); | cs |
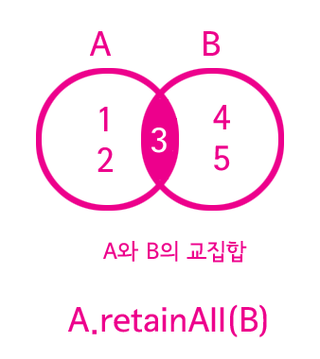
1 2 3 | 교집합(intersect) A.retainAll(B) | cs |
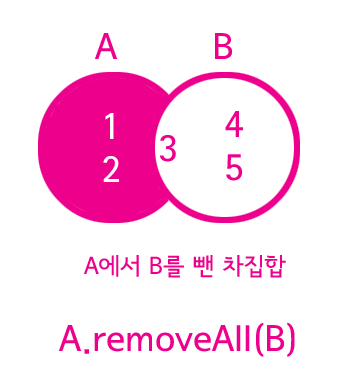
1 2 3 | 차집합(difference) A.removeAll(B); | cs |
 https://opentutorials.org/course/1223/6446
https://opentutorials.org/course/1223/6446
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 배열 (Array) / forEach (0) | 2017.02.26 |
|---|---|
| HashSet<E> / TreeSet<E> (0) | 2017.02.26 |
| Iterator 반복자 (0) | 2017.02.26 |
| List<E> / ArrayList<E> / LinkedList<E> (0) | 2017.02.26 |
| 이스케이프 시퀀스(Escape Sequence) (0) | 2017.02.26 |